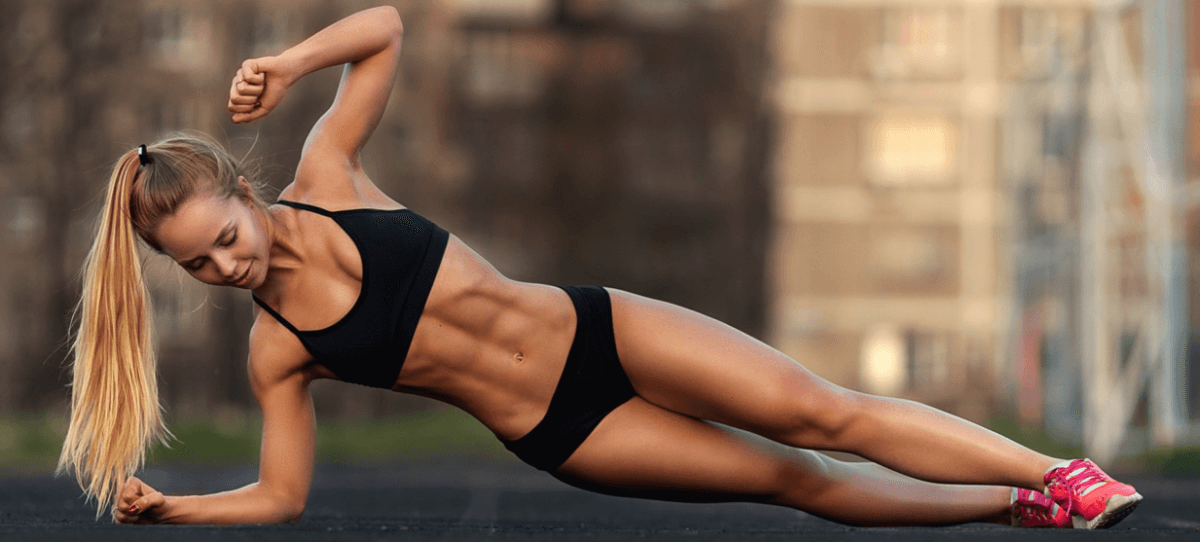
Lose weight the smart way
by Co van Well
How do you create a weight loss plan? This is often the first hurdle on the way to a slim body. Many people have a rough idea of how to go about it, but go wrong if they want to unify all parts of their strategy. Some hope that a magic pill does the job for them and don't pay enough attention to exercise and diet, others are again religious with their training but neglect their nutrition, yet another group watches every bite but damn it to get moving ... It is clear: the success of a weight loss plan is not based on one factor but depends on three important pillars: nutrition, exercise and supplements. How do you combine those three components into a joint approach? That is the theme of this article.
Nutrition:
If you want to lose weight, you have to eat less than you burn. This sounds so simple, but many people already make mistakes here. If you have no idea how much kcal you consume in a day, you can never prepare a good diet. So every plan starts with calculating your energy needs. The two most common methods to calculate this need are Harris-Benedict's formula and Katch-McArdle's formula. Tap on Google the name of either formula and you will find all kinds of calculators where you can enter your data. Within 1 minute you will find out what your kcal needs are. If you know what your fat percentage is, it is best to use the Katch-McArdle formula, if you do not know that, choose the Harris-Benedict formula.
Katrien wants to lose weight. She is a 30 year old woman with a height of 1 meter 70 and a weight of 70 kilos. She does fitness twice a week and she goes for a run once a week. She calculates her calorie needs using the Harris-Benedict formula. She does this by entering her data into an online calculator, which gives the following result: BMR: 1492 kcal, Maintenance: 2052 kcal.
The BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate) indicates the number of calories that your body burns without being physically active. The activity level has been taken into account in the maintenance requirement. It is this second number that you start working with: with a food intake of 2052 kcal per day, Katrien would remain at her current weight. However, she wants to lose weight, so she is going to prepare a diet that consists of less than 2052 kcal per day.
If you have calculated what your daily energy needs are, you can prepare a diet with this information in hand. To lose weight you need to eat less than your maintenance requirement. The question now is: how much less? If you sit too much under your need, you will feel weak and lifeless. Often you will also lose muscle and strength, which slows down your metabolism. This is because muscles constantly need nutrition, so the more muscle you have, the more you can eat. A “crash diet” is therefore counterproductive: in addition to fat, you also lose a lot of muscle mass, which reduces your combustion. As a result, your weight will shoot up again as soon as you don't stick to your starvation diet. After all, the loss of muscle mass has given you the metabolism of a snail.
So you want to eat less than your maintenance requirement, but not too much less. A good starting point is to consume 20-25% fewer calories than your maintenance level. With this amount you will burn fat without feeling bad or "eating up" your muscles.
Katrien's maintenance requirement is 2052 kcal per day. She now wants to eat 20% less: 2052 x 0,2 = 410,4 kcal
2052 - 410 = 1642 kcal
Katrien will then prepare a diet that counts about 1642 kcal per day.
Now that you have calculated how much kcal you will eat daily, you can set up the actual diet. What should this diet consist of? As long as you are in a negative energy balance, it strictly doesn't matter what you eat. Whether you get your kcal from McDonald's fast food or from cod fillet, brown rice and broccoli: as long as you eat less than you burn, you lose weight. Still, there's a lot to be said for choosing certain foods when dieting. Not only is this healthier, it will also make losing weight easier and you will lose more fat and less muscle.
The so-called “macronutrients” that make up food are proteins, fats, carbohydrates and alcohol. Protein play a crucial role within this group, especially in weight loss. In theory, your body can do without fats, carbohydrates and alcohol, but without protein in the diet, your body will not last long. By including a high proportion of protein in your diet, your approach will be more successful: at least 25% of the total number of calories or 2 grams of protein per kilogram of lean muscle mass is a good guideline. You can calculate the lean muscle mass (LBM - Lean Body Mass) if you know your fat percentage. You then subtract the weight of body fat from your total weight. Someone of 100 kilos with a fat percentage of 10% therefore has a lean muscle mass of 90 kilos.
What are, in a nutshell, the benefits of a high protein content in the diet? First of all, proteins are essential for building and repairing body tissues, including muscles. With a shortage of protein, muscles will be broken down. This means, among other things, a decrease in your metabolism. In addition, proteins ensure a stable blood sugar level and a feeling of fullness. This makes you less hungry, which makes losing weight a lot easier. In addition, proteins directly increase the metabolism. It costs the body to digest more energy proteins than carbohydrates, fats or alcohol. With a higher protein content, your metabolism is stimulated to burn more fat! Good sources of protein include fish, lean meats, poultry, cottage cheese, eggs, and protein powder.
In addition to proteins, a balanced diet will also contain fats and carbohydrates. For a long time it was proclaimed that fats in the diet were out of the question if you wanted to lose weight. Today, carbohydrates are often denounced. Neither view is correct. Choosing the right fats and carbohydrates is what it's all about. The fats should mainly be of the unsaturated type as found in fish, nuts, avocados and olive oil. The predominantly medium chain fatty acids in coconut oil are also healthy. In terms of carbohydrates, unprocessed products are preferred. Complex carbohydrates keep the blood sugar level more stable and provide energy for longer, making them preferable to sugars. Good carbohydrate sources are vegetables, oatmeal, rice cakes and brown rice. Alcoholic drinks provide extra kcal in the form of carbohydrates (4 kcal per gram) and alcohol (7 kcal per gram) and should therefore be consumed in moderation during a diet.
Katrien wants at least 25% of the calories in her diet to come from proteins. Her diet counts 1642 kcal: 25% of 1642 kcal is 410 kcal, a gram of protein provides 4 kcal, so 410 kcal equals about 100 grams of protein. She mainly gets the remaining kcal from unsaturated fats and complex carbohydrates. The total should be approximately 1642 kcal. Katrien prepares the following diet:
Breakfast:
-50 grams of oatmeal
-100 grams of fruit (pineapple, berries, pear, apple, mango)
-50 grams “Iso whey"
The ingredients are made into a shake in the blender with water.
445 kcal / 48 grams of protein / 7 grams of fat / 52 grams of carbohydrates
Inbetween:
-1 apple
60 kcal / 0 grams of protein / 0 grams of fat / 14 grams of carbohydrates
Lunch:
-100 grams of smoked salmon or trout fillet
-1 whole wheat pistolet
-Lettuce and tomato for garnish
320 kcal / 30 grams of protein / 12 grams of fat / 23 grams of carbohydrates
Inbetween:
-4 multigrain rice cakes
-50 grams of 20+ cheese or 100 grams of cottage cheese
-Lettuce and tomato for garnish.
265 kcal / 16 grams of protein / 6 grams of fat / 34 grams of carbohydrates
Supper:
-150 grams of chicken or turkey fillet or 200 grams of cod, tilapia or panga fillet
-50 grams of whole wheat pasta or rice or 4 small potatoes (= 200 grams)
-300 grams of vegetables (salad, broccoli, bell pepper, etc.)
-1 tablespoon of olive oil (for baking)
-100 grams of vegetable pasta sauce
515 kcal / 51 grams of protein / 14 grams of fat / 45 grams of carbohydrates
Total: 1605 kcal / 145 grams of protein (= 36%) / 39 grams of fat (= 22%) / 168 grams of carbohydrates (= 42%) / 0 grams of alcohol (= 0%)
Katrien decides to follow this diet 6 days a week and to “sin” on Sunday with some tasty snacks. This way she keeps the diet better.
It is best to use a special software program to compose a diet. All you have to do is enter your nutrition and the program calculates the calories, proteins, carbohydrates, fats and vitamins and minerals. Different versions can be found online. For example, the Nutrition Center has released the Dutch-language program “Eetmeter”. In English, the free program Cron-O-Meter is very user-friendly. FatSecret's “Calorie Counter” is a useful tool for smartphones.
Now that you have prepared the diet, you can start. If your calculation is correct you will lose weight at a steady rate. The first week of your diet decreases you often see the biggest difference on the scales. In part, this is water that you lose when your body stores fewer carbohydrates. Each gram of glycogen (the name for stored carbohydrates) binds about 4 grams of water. After the first week, a rate of one kilogram of weight loss per week can be maintained. If you lose weight much faster, you should check whether you are not eating too little and therefore losing muscle mass.
Over time, weight loss will slow down or even come to a complete stop. This is the point where you lower your calories a little further. Only reduce the number of carbohydrates and / or fats and not the proteins! The proportion of proteins will therefore only increase and not decrease during a diet! You stick to the new, modified diet until you reach the next plateau and the calories change slightly. However, you can also leave your diet undisturbed and increase the amount of exercise and / or take a fat burner. Both factors are discussed below.
Movement:
Increasing the amount of exercise increases your energy needs. With a consistent diet, you will thus stimulate fat burning.
After a month of following her 1600 kcal diet, Katrien notices that fat burning is slower. She can now lower the calories further, but she prefers to exercise more and still burn fat. Until now, Katrien has been doing fitness twice a week and jogging once a week. Katrien now decides to exercise a third time a week and run twice a week.
Her maintenance energy requirement will rise from 2052 kcal to 2313 kcal per day according to the Harris-Benedict formula. Because Katrien leaves her diet unchanged, she again finds herself in a negative energy balance and she loses weight again.
The combination of strength training and cardiovascular training is the golden combination for weight loss. Through strength training you build muscle mass so that your metabolism is higher throughout the day. Even if you are sitting on the couch watching TV: thanks to your weekly play with the weights you now burn extra calories. Through "cardio" such as running or cycling you burn a lot of calories during exercise, but less at rest. A lot of cardio without strength training can even be counterproductive: you lose muscle, which slows down your metabolism and makes it increasingly difficult to burn fat.
"Do I have to adjust my strength training if I go on a diet?" is a frequently asked question. Look around you in an average gym and you will see that many dieters train at a fast pace and do a lot of repetitions. The logic behind this is that they burn more calories this way. The idea is just not correct: by increasing the training rhythm and lowering the weights, the muscles do not get the same stimulation as before. Because the muscle will not get the same stimulation now, it will become thinner. With the loss of muscle mass, your metabolism will also slow down. This modified form of training does not lead to one elevation but one reduction of your fat burning.
Two other frequently asked questions about training during a diet are: "Do I have to maintain a certain pace to burn maximum fat?" and “Does it matter if I do cardio? ”. The first question can best be answered on the basis of the experience that Katrien gains.
Normally Katrien does her running laps at a fast pace to improve her condition. Now she heard at the gym that you burn more fat if you are not completely out of breath when walking but exercise in a lower heart rate zone. For that reason Katrien slows down her pace to jogging slowly. After her usual hour, she calls it quits. She has burned 420 kcal in this hour. Of this, 252 calories (60%) come from fats.
During her normal hour of running at a high pace Katrien burned 750 kcal. Of this, 300 calories (40%) came from fats.
Not only did Katrien burn more calories while running at a high pace, she also burned 48 more calories from fat and built up a better condition.
Cardio is therefore best done with a higher heart rate. Alternating high and low intensity in the form of interval training is also very effective. In addition to the above-mentioned benefits, a plus of this is that it is time-saving and increases the metabolism for the rest of the day beyond cardio at a leisurely pace.
Regarding the second question “Does it matter if I do cardio? Opinions are divided. Some athletes prefer to do cardio on an empty stomach, for example before breakfast, because it would have the advantage of burning more calories from fat in the absence of food. It is also a good time for cardio after strength training. You do the weight training when you are at its strongest. By only doing cardio after the strength training, your blood sugar level has also dropped, so that you would burn more fat.
The important thing is not when you do the cardio but that you do it. Ultimately you need to be in a negative energy balance at the end of the day if you want to lose fat. The extra cardio burn, when you do it, can be the deciding factor.
Supplements:
Supplements can make all the difference. By using the right products, the chance of your diet being successful will increase. What are useful supplements to get if you want to lose weight? First of all, there are of course the well-known “fat burners”, products that, as the name suggests, aim to stimulate fat burning. The strongest weight loss products, such as Axelamin from IQ Nutrition, put your body in a “higher gear”, as it were; your sympathetic nervous system is more activated, causing your heart rate to increase, your body temperature to rise, you have less appetite and your activity level to increase. The net result is an increased calorie burn. A nice side effect of these products is the energy they provide. If you take a capsule half an hour before training, you can be sure that you get the most out of it, even on a calorie-restricted diet. Commonly used ingredients in this class of “fat burners” include synephrine, l-tyrosine and caffeine.
Seven weeks after starting her diet, Katrien notices that the fat burning is not as fast as she would like. The first month, an adjustment of her diet was enough to lose weight. Then she started exercising more to stimulate the metabolism and now, a few weeks later, she threatens to reach a plateau again. Katrien has no time for more exercise and she doesn't like eating less, so she decides to take an Axelamin capsule twice a day. Now those last pounds also fly off.
People with high blood pressure or heart complaints should opt for the milder weight loss products. Even people who cannot stand the energetic effect of the stronger means are wise to make a different choice. T + from IQ Nutrition is an example of a “mild” yet very effective weight loss product. Slimming supplements that are well tolerated by everyone contain, for example, chromium, l-carnitine, coleus forskohlii, guggul and green tea extract.
Protein supplements are another useful addition to a diet. As said, someone who wants to lose weight is wise to give proteins a prominent place in their diet. These proteins can partly be obtained from sources such as chicken fillet, cottage cheese and fish. Protein powder is a very high-quality addition to this. And very practical, too: you can prepare a delicious shake within a few seconds. The choice of protein types is so overwhelming nowadays that the consumer sometimes cannot see the forest for the trees: there is whey, casein, soy, egg protein, pea protein and mixtures of different types. Each product has its specific advantages. For example, whey (“whey” in English) has a high concentration of the so-called “essential amino acids” that are important for building and recovery. An example of this is “Iso whey”. This product not only has a very favorable amino acid profile, it is also free from fat and carbohydrates, making it the perfect addition to weight loss. Casein-based protein supplements also have their place in a diet. Casein gives a more satiated feeling and the blood sugar level remains more stable than is the case with whey consumption. Two benefits that come in handy when you are on a diet. Casein-based supplements such as “PM” are also excellent to take before going to sleep because they are digested more slowly and thus ensure a sustained release of amino acids during the night. For people who cannot tolerate lactose or milk protein, there are also many options today. There are products based on egg protein, soy or pea protein, such as the “Protein Shake” from VNM Premium Series.
Supplementing the diet with amino acids can promote recovery during a diet. Amino acids also prevent muscle breakdown. You can choose a product that contains all amino acids, or a supplement that consists of specific amino acids. The latter category includes BCAAs: these are three essential amino acids known for their anabolic and anti-catabolic properties. The intake of amino acids, including BCAAs, is especially useful after, and possibly before, training. Because they are rapidly absorbed by the body, they immediately start their recovery work and thus limit muscle damage to a minimum.
A multivitamin and mineral preparation and Omega 3 capsules keep the body in optimal condition all year round. Precisely with an energy-restricted diet, deficiencies are lurking. A strong “multi”, such as the Special Two from Now, contains all vitamins and minerals in a high dose. Moreover, the product is easily absorbed by the body. Something that is almost always lacking in the cheaper multivitamins. A majority of the Western population does not get enough Omega 3 fats. These fatty acids, which are found in oily fish, are indispensable for many bodily functions such as keeping the heart and blood vessels healthy, the functioning of the brain and inhibiting inflammation. They also play an important role for the metabolism: they increase insulin sensitivity and the use of fat as fuel. Omega 3 is therefore also a real weight loss supplement.
The best results are achieved by drawing up a plan that takes into account diet, exercise and the use of supplements. In other words: the whole is more than the sum of its parts. Also when losing weight.